Entropy and compositional spots
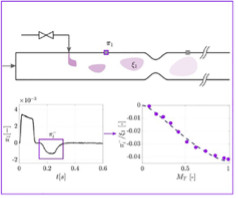
Recent experiments have confirmed previous theories of the generation of entropic and compositional noise through choked and unchoked nozzles. These are acoustic disturbances associated with the change in gas properties as they propagate through an accelerating flow such as in a gas turbine nozzle.
Reference
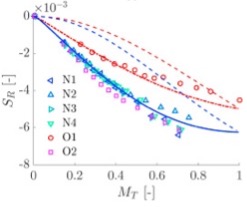
First direct measurement and model comparison of compositional noise through a subsonic nozzle: this concludes the generalisation of the entropy and compositional model tests. Compositional and entropy indirect noise generated in subsonic non-isentropic nozzles. F De Domenico, EO Rolland, J Rodrigues, L Magri, S Hochgreb, Journal of Fluid Mechanics (2021) 910, A5.
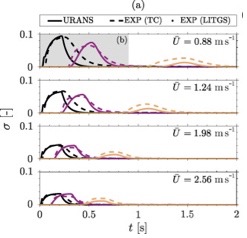
The work used CFD to simulate the experimental dispersion of the temperature (entropy) pulse through the nozzle. Numerical investigation on the generation, mixing and convection of entropic and compositional waves in a flow duct. J Rodrigues, A Busseti, S Hochgreb, Journal of Sound and Vibration (2020) 472, 115155.
Experimental simulations and models of the generation of sound via entropic (temperature) perturbations with different shapes of nozzles, and a modified model including acoustic losses. A generalised model for acoustic and entropic transfer function of nozzles with losses F De Domenico, EO Rolland, S Hochgreb, Journal of Sound and Vibration (2019) 440, 212-230.
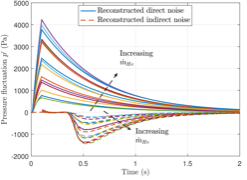
These were the first direct measurements of compositional acoustic perturbations generated through a nozzle. Direct and indirect noise generated by entropic and compositional inhomogeneities (2018). EO Rolland, F De Domenico, S Hochgreb, Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power 140 (8), 082604.
These were the first direct measurements of temperature (entropic) acoustic perturbations generated through a nozzle. F De Domenico, E O Rolland, S Hochgreb, Detection of direct and indirect noise generated by synthetic hot spots in a duct. J. Sound Vib. (2017) 394:220-236
E O Rolland, F De Domenico, S Hochgreb. Theory and application of reverberated direct and indirect noise. Journal of Fluid Mechanics (2017) 819: 435-46.